Plant frost resistance zones in Russia, why they should be taken into account when choosing varieties

By purchasing new seedlings It is necessary to pay attention to which winter hardiness zone they belong to.
Having accurate information about which of them the area of your residence belongs to, you can be completely sure whether rose bushes or other plants in the open ground will be able to survive the winter.
The article will help you understand the concepts of climatic zones, learn about the factors for determining winter hardiness zones, and explain the reasons why you need to pay attention to the frost resistance characteristics of plants.
Content:
- Climate zones
- Frost resistance zones - what are they?
- Factors determining the frost resistance zone
- Why you should pay attention to the winter hardiness characteristics of plants
Climate zones
Our planet has a varied climate. This happens because it is unevenly heated by the sun, and also due to uneven precipitation.
Proposals for classification climate began to arrive back in the seventies of the 19th century. B.P. Alisova, then a professor at Moscow State University, divided climate into seven types, which together make up the planet’s climate zone. The professor expressed the opinion that four belts are main, and the remaining three are connecting between the main ones - transitional.
A little later, in 1900, Vladimir Koeppen identified 6 main climatic zones:
- A is a belt of humid tropics in which there is no winter;
- B - zone has a dry climate, there are two of them - on both sides of the equator;
- C – with moderately warm temperatures throughout all seasons; regular snow cover is not typical for this zone;
- D – two boreal belts climatehaving clearly defined boundaries between the summer and winter periods;
- E – zones close to the Arctic Circle with a snowy climate.
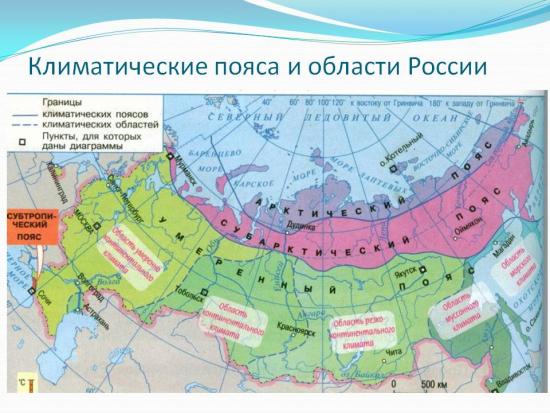
Today, climate zones are divided into 4 main ones:
- equatorial;
- tropical;
- moderate;
- polar.
And three more belts are transitional:
- subequatorial;
- subtropical;
- subpolar.
Frost resistance zones - what are they?
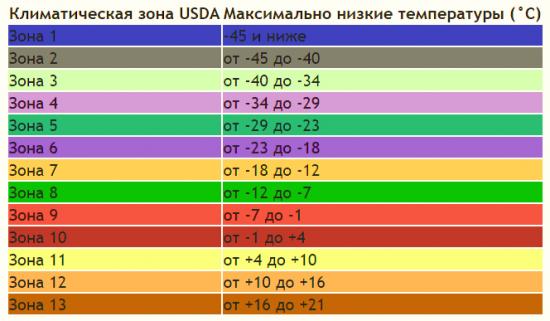
Initially, the division of climatic zones into frost resistance plants were produced by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Agriculture needed this.
13 zones were identified. The basis for their identification was the lowest temperature indicators during winter. After that, this development was subject to revision and improvement for a long time.
Zoning of North America is designated taking into account the climatic characteristics of mountainous and coastal regions. Over time, frost resistance zoning was developed for the European continent.
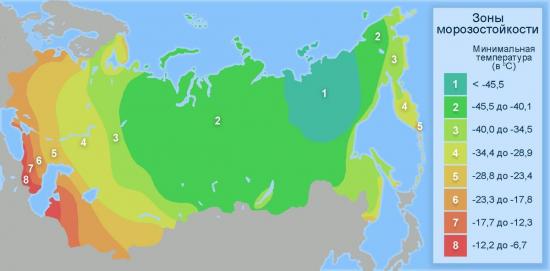
Plant frost resistance zones in Russia have approximate values. They cannot be considered a full-fledged recommendation for banning the cultivation of certain plant species. Be that as it may, gardeners would benefit from knowing that their region belongs to frost-hardiness climatic zones.
Factors determining the frost resistance zone
The lowest temperature readings during the winter period in a particular area are influenced by geographic latitude, terrain, location in relation to the ocean, its warm or cold currents and air humidity.
The amount of radiation received by the Earth from solar radiation depends on latitude. It is maximum at the equator, which is why the climate is hottest there. But this is not the determining factor.
For example, the geographic latitude on which London is located is north of the latitude on which Kyiv is located, but in Kyiv in winter there are often frosts, during which thermometer readings drop below minus 20 degrees. It belongs to hardiness zone 5 and in southern England the grass turns green during winter.
It belongs to frost resistance zone 9, because the Atlantic and Gulf Stream, a warm current, are nearby.
The southern coast of Crimea belongs to zone 7, and its steppes – to 6. The coast of the peninsula is protected from the northern winds by mountains, for this reason such heat-loving plants grow there as magnolias, palm trees, wisteria and cypresses.
Zoning of Europe according to frost resistance is distributed from western to eastern latitudes. The Atlantic has such an influence on the distribution. Western Europe has a milder climate compared to Eastern Europe.
Why you should pay attention to the winter hardiness characteristics of plants
At the time of purchase seedlings In the nursery, many people pay attention to the fact that the plant indicates that it belongs to the winter hardiness zone. This helps determine at what winter temperatures the plant will not die.
A plant that, by its natural characteristics, is adapted to grow in one zone will feel poorly or die in another, colder or hotter one.
Some of the plants are quite capable of withstanding a decrease in temperature, but cannot tolerate excess moisture that forms during winter thaws in severe conditions. soils. And other plants easily survive harsh winters due to high snow, which protects their root system from frost. The same effect can be achieved with autumn mulching.
Based on the results of all of the above, we can conclude that heat-loving palm trees will not grow in open ground near Moscow, and cloudberries will not grow in Adler.
Before planting any plant on your personal plot, you need to study its natural habitat, temperature conditions characteristic of that area and quality soils.
And also useful information about climate zones for summer residents, watch the video:











Comments
To prevent trees and shrubs from freezing in winter, you need to buy zoned seedlings or cover them for the winter. True, this will be difficult to do with trees, but bushes and vines can be protected.
Previously, I bought plants for my garden plot and didn’t even look at what climate zones they were intended for. Now I'll be more attentive. Indeed, some trees grow well and bear fruit and endure winter easily, but for some it is difficult to get along here.
It is imperative to buy plants for frost-hardiness zones, otherwise they simply will not grow or will freeze in the winter. My neighbor in the Moscow region grows grapes, watermelons, and melons very well. They are zoned.
We always chose zoned varieties of plants for planting, but we also tried to grow more heat-loving crops in the Moscow region, although the results were different depending on the winter.
A couple of years ago I picked myself some bulbs of tulips, lilies, and daffodils - I spent a lot of money, hoping to have some beautiful varietal flowers at my dacha. But nothing came of them. Perhaps this can be explained by the fact that careless suppliers are chasing profits and do not take into account the climatic conditions of planting material when purchasing everything?