Alternation of crops on the site: what can be planted in the garden after that
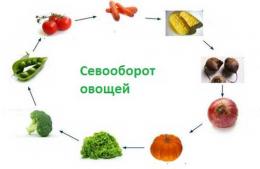
The principle of changing crops or crop rotation has been known to farmers for a very long time. In the old days, this technique of temporary and territorial alternation of plants was called multifield. In addition to changing crops, one of the fields was very often left unsown, that is, the land was kept fallow. With the development of science, multi-field farming has received justification from the point of view of agrobiology, agrochemistry, and economics.
In small areas, organize a complete crop rotation, including fallow, it is unlikely to work, however, we will try to find out what can be planted in the garden after that. This will help you maintain proper crop rotation.
Content:
- What does the correct change of crops in the garden give?
- How to properly organize crop rotation in the garden
- Vegetable compatibility, crop rotation and supporting measures
What does the correct change of crops in the garden give?
When a person receives a plot of virgin, previously uncultivated land for use, then in the first three to four years of growing garden crops on it, they produce a good harvest. In the next two to three years, subject to the application of fertilizers, mineral and organic, the harvest continues to remain very decent. However, several years after the start of cultivating vegetable and other crops, their quantity and quality begins to decline steadily.
No fertilizers or soil cultivation methods give the desired yield and lead only to short-term, unstable improvements. Practical observations showed that if crops were changed at least once every two to three years, the yield improved both quantitatively and qualitatively.
However, this technique was also not always effective. It turned out that both predecessor plants and neighboring plants play an important role. If you organize the change of crops correctly, you can achieve the following positive results:
- increase crop yields by 20 - 25%
- reduce fertilizer costs
- minimize or completely eliminate diseases and pests
- reduce physical and material costs
In addition, the inclusion in the cultivation of the garden of such a technique as sowing green manure plants helps both clear the area of weeds and serve as a means of fertilizing the land and enriching it with mineral and organic substances. If you do not adhere to the order of alternating crops on the site, this is fraught with the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms and pests in the soil. Failure to follow the order and planting plants after unfavorable predecessor crops depletes the soil and increases the cost of fertilizers.
How to properly organize crop rotation in the garden
To properly organize the rotation of grown crops, you need to adhere to several rules. One of them is not to plant like after like. It follows from this that one should not just not plant, for example, potatoes after potatoes, but any plants from the nightshade family should not be planted after each other.To comply with this rule, you need to know that all plants are divided from the point of view of botanical taxonomy into families, each of which includes several species of cultivated plants.
Family Solanaceae
Plants of this family include crops that are very important for every gardener:
- potatoes
- tomatoes
- vegetable sweet and hot peppers
- eggplant
- tobacco
- physalis
This family also includes flowers such as petunia and decorative varieties of dope. If the site is supposed to grow several nightshade crops, then all of the above vegetables and flowers should not be planted one after another. This is due to the fact that these plants primarily take available nitrogen from the soil and greatly deplete it.

If tomatoes or eggplants grew this year, then next year you should not plant potatoes in the same area. Now other plants from the Solanaceae family have appeared in cultivation, such as:
- Saraha
- sunberry
- naranjilla
- melon pear
- cocoon
Although for many they are still exotic, they are gradually occupying their niche in the areas.
Pumpkin family
This family includes both well-known names and plants unfamiliar to many:
- cucumbers
- pumpkin
- watermelons
- melons
- squash
- zucchini
- zucchini
- chayote
- Lagenaria
- luffa
These plants consume quite a lot of not only organic matter, but also phosphorus and potassium from the soil.
Brassica family
This family includes not only all types of cabbage, but also other garden and agricultural plants:
- mustard
- horseradish
- rape
- turnip
- saffron milk cap
Some of the family members can be used as green manure crops.
Family Legumes
Plants of this family are distinguished by their ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere.Legumes include:
- lentils
- peas
- chickpeas
- beans
Some plants can also be grown as green manure and plowed into the ground.
In addition to the above families, it is worth remembering other cultures, such as:
- Umbrellas - carrots
- Amaryllidaceae - onion, garlic
- Amaranthaceae - beet
- Cereals - corn
- Asteraceae - sunflower
These plants can be both good predecessors and excellent neighbors for many vegetable crops.
Vegetable compatibility, crop rotation and supporting measures
Before the start of the gardening season, you need to think through a plan - a crop planting scheme. In conditions of limited space, it is more convenient to divide the territory into 4 parts. If you swap crops every year, then plants of the same family will end up in the same bed three years later on the fourth. In addition, it is desirable that the crops enter the garden after the best predecessors.
Video about crop rotation and the best neighbors on your site:
The best predecessors for vegetable crops in the garden
For crops from the Solanaceae family, the following plants will be the best predecessors:
- Onion
- peas
- cucumbers
- cabbage
The best neighbors will be:
- watermelon
- thyme
- tarragon
It is very good if you grow before any type of cabbage and other vegetables from the Brassica family:
- zucchini
- potato
- corn
- carrot
Good neighbors for them will be:
- dill
- celery
- mint
- chard
- spinach
It is best to plant before legumes:
- any cabbage
- turnips
- beets
- cucumbers
- vegetable peppers
The best neighbors for plants from the legume family:
- coriander
- radish
- pumpkin
- sunflower
- salad
If you need to plant pumpkin crops, then this should be done after:
- any cabbage
- garlic
- eggplant
- tomatoes
- spinach
It’s good to plant next door:
- rhubarb
- basil
- marjoram
- beets
- coriander
- corn
- sunflower
In addition to vegetable crops, you can also grow berries and shrubs in the garden. It is best to plant strawberries and strawberries after:
- dill
- Luke
- oats
- carrots
- peas

The berry will grow well next to:
- garlic
- cucumbers
- sorrel
For shrubs such as gooseberries and currants, the best predecessors will be:
- peas
- beet
- corn
The best neighbors for them:
- raspberries
- peas
If it is not possible to organize an annual change of crops, then it is allowed to grow vegetables on the same area for two seasons. In addition, the situation will be saved by sowing green manure before planting crops or after harvesting. For spring planting you can use:
- peas
- oats
- mustard
They do this immediately over the thawed ground. By the time the main crop is planted, spring green manure is plowed into the soil. In the fall, after the harvest is harvested, the following crops can be planted:
- rye
- mustard
- phacelia
When planting in autumn, green manure either goes under the snow and the ground is dug up in the spring, or in the fall they are embedded in the soil. It is advisable to record all manipulations related to the rotation of crops in the garden in a special diary, this will help to comply with the rules for changing crops on the site.