Types of plant propagation important for obtaining planting material
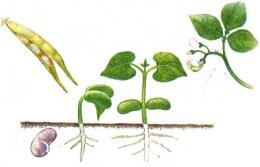
The life of all living organisms is designed in such a way that, having reached a certain stage of development, they must increase the population, giving life to a new generation. Plant organisms are no exception. Kinds reproduction plants are of practical importance when growing agricultural and garden plants, not only varietal and cultural varieties, but also weeds to determine adequate measures to combat it.
Despite the diversity of plant forms, several main types of reproduction can be distinguished that are characteristic of plants that are important to humans: vegetative propagation and generative propagation.
Content:
Vegetative propagation of plants
The formation of an independent new plant from the multicellular part of an adult specimen of the parent (maternal) plant refers to vegetative methods of propagation. Vegetative reproduction refers to the types of asexual reproduction. Both lower and higher plants and even mushrooms can reproduce vegetatively. A new plant can develop from a multicellular part of a mother plant:
- root
- sheet
- stem
And also from a modified escape:
- bulbs
- rhizomes
- tuber
- mustache
For the propagation of cultivated plants, vegetative propagation is relevant in cases where:
- it is impossible to obtain seed material
- plant grows too slowly from seed
- a plant obtained from seeds does not retain the characteristics of the mother
- you need to get planting material from a rare specimen
Vegetative propagation is inherent in both wild species and cultivated plants. And the ability to completely restore all organs from parts of plants is widely used in the cultivation of fruit, flowering, berry and other agricultural plants.
Propagation by cuttings

Cuttings are parts of shoots or roots from which a new plant is formed. Most trees, shrubs, and perennial herbaceous plants can be propagated by stem cuttings. The basic principle of propagation by stem cuttings - this is the production of roots on fragments of stems. Root cuttings are used to propagate plants that have accessory buds on their roots. This applies to raspberries, roses and some other plants.
Reproduction by layering and tubers
The method consists in the ability to obtain a separate plant from a shoot without separating it from the roots of the mother plant until it is completely rooted. The shoot bends and pins to the soil. After a few weeks, a root system appears at the point of contact with the ground and the upper part can be separated as an independent plant. Typical propagation by tubers can be observed when growing potatoes. Its tubers have buds - eyes. You can grow a new plant not only from a whole tuber, but also by cutting it into fragments with buds.
Reproduction by root shoots and leaves
New plants can grow from the roots of some plants - offspring, which are easily separated from the adult root and form as independent bushes or trees. An example of such reproduction is bird cherry, even if you cut down the ground part, after some time numerous shoots of young bird cherry will appear on the surface.
In a number of plants, you can get a new plant from a leaf with a cutting. For example, this is how you can propagate gloxinia or violet when a leaf with a cutting is either planted in the soil or takes root in water. You can also get a new plant by grafting cuttings or buds onto another plant, or when daughter bulbs appear on the mother bulb, or by separating parts of onion scales. All plants obtained through vegetative propagation are exact clones of the mother specimen and have all its properties.
Generative plant propagation
Reproduction of plants using seeds is called generative. Generative reproduction can be either sexual, with the participation of male and female germ cells, or asexual.
Sexual and asexual reproduction
Higher plants such as horsetails, mosses and ferns form special organs - sporangia, in which spores develop, and from them gametophytes are obtained. At its core, a gametophyte is a completely independent plant obtained from cells of the same species. Sexual reproduction makes it possible not only to obtain seeds of most cultivated plants, but also to conduct breeding work.
Sexual reproduction of plants is possible due to specialized male and female reproductive cells. Male sperm cells mature in specialized organs - anthers.
Female eggs in plants mature in the ovary of the pistil. The process of fertilization in plants is quite complex and depends on many conditions. In flowering angiosperms, seeds are formed after double fertilization.

The results of sexual reproduction are the appearance seeds. New plants obtained from seeds may exhibit the characteristics of the parent forms, but may also differ from them. Selection work to develop new varieties and hybrids is based on this property of sexual reproduction. Seed propagation is inherent in all life forms of plants:
- trees
- bushes
- herbaceous perennial
- herbaceous annual
The main condition for growing plants from seeds is to embed them in the soil and create conditions for germination. As a rule, most plants have both vegetative and seed propagation. Also, all cultivated plants have access to the same types of reproduction as wild plants. In addition to the above, there are other natural and artificial methods of plant propagation.
Diaspores, tissue culture, brood buds
Many plants have adapted to form from special brood buds almost ready-made miniature copies of themselves with rosettes of leaves and roots, or miniature nodules, which, upon germination, give rise to a full-fledged plant. Brood buds can be located on leaves or in inflorescences. Falling on priming, the brood bud gives rise to a new plant. This way they can reproduce:
- lilies
- garlic
- bows
- bryophyllum
- ferns
This type of propagation is classified as vegetative; it is inherent in plants where, due to weather and climatic conditions, the seeds may not have time to ripen.Separately, it is worth mentioning this method of reproduction as tissue culture. This is perhaps the most productive method of obtaining new plants. Tissue culture is also a vegetative method of propagation, although only one cell obtained from the tissues of the mother specimen gives rise to a new plant. Whereas in other types, a new plant is grown from multicellular parts.
At its core, tissue culture is an example of cloning. To do this, take the tip cells from growing shoots and placed in a nutrient medium. And although today this is a rather labor-intensive and expensive process, it is possible to obtain an almost unlimited amount of planting material in the laboratory. In addition, all plants obtained by this method are completely sterile and free from any diseases or pests.
All about types of plant propagation:
Interesting information about the vegetable garden










