What is saltpeter made from, how is it used in crop production, storage features

Saltpeter – one of the most famous and widespread fertilizers with good efficiency indicators, saturation of plants with useful substances and at the same time low cost. It is precisely these qualities that attract many plant growers and gardeners who constantly use fertilizing in their plots and everyone, undoubtedly, is interested in what saltpeter is made from.
Content:
- How is ammonium nitrate produced?
- Type of fertilizer
- Use as nitrogen fertilizer for plants
- Applications for disease control
- Does saltpeter contain nitrates?
- How to ensure proper storage of saltpeter?
How it is produced
What is ammonium nitrate made from? NH4NO3, also known as ammonium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, contains the main element - nitrogen. Moreover, it contains 26-34%
Another important component is sulfur. Can range from 3% to 14%. The formula is as follows: NH3+HNO3->NH4NO3+Q
This substance is produced in chemical plants using nitric acid and ammonia, using chemical reactions between compounds.
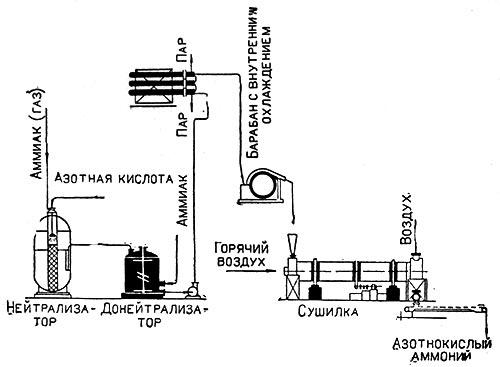
All production consists of the following stages:
- The acid is neutralized by ammonia in the gaseous state.
- The resulting solution evaporates for some time.
- Ammonium nitrate goes through a crystallization stage.
- The salt is dried.
First, the raw materials are sent to the neutralization department.As a result of strong interaction, a lot of heat is released, part of the liquid evaporates, and the other part (the resulting water vapor) is removed.
The slightly evaporated solution passes into another apparatus - the final neutralizer, in which the neutralization of the acid is completely completed.
The resulting liquid flows into a unit where a vacuum apparatus operates and evaporates the solution at low pressure. The evaporation process continues until the required concentration is reached - 98%.
Ammonium nitrate crystallizes on a drum, which is constantly cooled. The crystals turn into a crust, which is then cut off and sent to dry.
They are dried on special drums at a temperature of 120 degrees, after drying is completed, the raw materials are transported to packaging. Often, to reduce the caking and hygroscopicity inherent in saltpeter, a number of other components are added to its composition.
In ancient times, obtaining ammonia saltpeter occurred in a more natural, but labor-intensive way; currently production has a wide scale and a clear sequence of stages.
Factories produce ammonium nitrate of several types:
- scaly, in this form it strongly absorbs moisture from the air, as a result of storage it cakes and does not crumble;
- granular is produced in special “towers” where it is sprayed by a centrifuge and subsequently hardens to form granules. Granular is more convenient to use, easily distributed throughout the field during fertilizing, and does not stick together.
Type of fertilizer
We found out what ammonium nitrate is made from, but besides this, there are many types of this fertilizer, which are obtained by adding ammonium nitrate to the finished product to improve physical qualities and depend on the purpose of use.

Simple
This variety provides the main thing for plants: it saturates them with the macronutrient nitrogen for full growth and development. Nitrate ammonium is used in many countries of the world and has long proven effective for most crops. This species perfectly replaces mineral fertilizers such as urea.
Brand B
There are 3 varieties that are ideal for home use. Sold in convenient pre-packaged bags, it easily saves indoor plants from wilting and drying out by saturating them with nitrogen.
Ammonium-potassium (K2NO3)
Known as "Indian salt". The most effective type for spring feeding of garden trees, application to the soil before sowing tomatoes and their further feeding.
Lime salt (Norwegian salt)
Available in granular and plain form. Contains calcium potassium, magnesium. The granules are very durable, absorb little moisture, so they are stored well. The composition is treated with fuel oil, which is not very advisable to use on your plots and gardens, because fuel oil remains in the soil for a very long time until it completely decomposes, causing great harm.
Calcium

Available in liquid and dry form, it contains calcium.
Magnesium (magnesium nitrate - aqueous)
Saturates the soil with essential magnesium, especially suitable for legumes and vegetable crops.
Porous is the most dangerous variety, which is used not for feeding the soil, but for the production of explosives.It absorbs moisture very strongly and reacts violently with it.
Use as nitrogen fertilizer for plants
The range of applications of this fertilizer is wide:
- for feeding colors, various shrubs,
- fertilize fruit trees, vegetable crops and root crops.
Plant growers often use it to obtain good seedlings. It is relevant to use even during the active growing season. In addition to vegetable growing and gardening, it is also used in indoor floriculture, combined with potassium salt. It is effective both in the summer months and during the winter dormancy period, which is its distinctive feature.
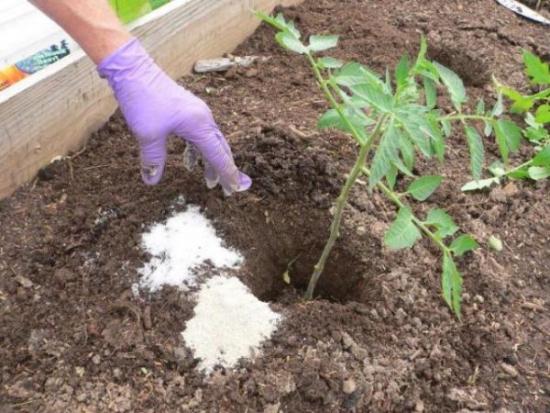

There is a requirement for the depth of application - at least 10 cm. Application measures depend directly on the initial composition and quality soilThe worse it is, the more fertilizing will be required, 40-50 g per 1 sq. m. For nutritious soil you need no more than 25 g per 1 sq. m.
The application rate also differs depending on the type and variety of the plant. Vegetable crops are fed at least twice: before the first buds appear and after the fruits appear, 5-10 g per 1 sq. m.
Root crops require 6-7 g of the substance per 1 sq. m; for them, granular fertilizer is distributed in small ditches between the rows to a depth of 3-4 cm three weeks after the appearance of the first shoots. Fruit trees need a larger amount, and it is applied with the blossoming foliage. 30 g of the substance per 10 liters of water are thoroughly mixed and poured under the root. During the period of ripening of berries on bushes, they are fed in the proportion: 50 g of dry fertilizers for 10 liters of water. It is advisable to carry out such feeding systematically, at least twice a month.
It is worth noting that you must adhere to some rules for using fertilizer:
- Shared use with organic substances: peat, straw, sawdust, chalk, dolomite. This can lead to the most unfavorable consequences: during reactions between substances, they can ignite.
- Indoor plants are fed until the first buds appear.
- Decorative deciduous trees need to be fertilized during the period of active growth of green mass.
- An excess of fertilizers affects plants much worse than a lack of certain substances, and this must always be taken into account and the norms and timing of application must be observed.
After entering the soil, nitrogen mineralized by microorganisms from ammonium nitrate begins to be quickly absorbed by plants. Each time a substance is added, it is necessary to water the crop abundantly so that the saltpeter dissolves better and reactions with the absorbing soil complex begin.
If the soil lacks calcium, temporary acidification occurs after fertilizing with ammonium nitrate soil:
- On soils with high acidity, acidification can be reduced and the quality of the soil can be improved using liming;
- Soddy-podzolic soils require the application of neutralized or lime-ammonium nitrate.
- Due to the content of bases, sierozems and chernozems do not become acidified. For such types of soil, ammonium nitrate is one of the best and most effective fertilizers.
Applications for disease control
Ammonium nitrate, in addition to its direct purpose - saturating the soil with nitrogen, protects plants from many diseases and increases their resistance to disease. If the crop rotation scheme is not implemented correctly, or if a monoculture is grown in place for a long time, the number of pathogenic fungi increases significantly, leading to crop damage.
The best prevention of this phenomenon is to observe crop rotation, treat the area with disinfecting compounds, for example, a solution of potassium permanganate, and apply ammonium nitrate during plowing in the spring. This technique allows you to increase the immunity of crops, which simply will not allow large colonies of fungi to multiply.
In addition, ammonium nitrate normalizes the processes of photosynthesis in the green part of plants, improves the structure of tissues, stimulates active “breathing,” and increases the storage rates of already harvested crops.
Does saltpeter contain nitrates?
Each of us knows that the nitrate content in vegetables, fruits and berries are harmful and dangerous for the human body. Ammonium nitrate is a prominent representative of nitrate fertilizers.
But few realize that ordinary organic fertilizer: peat, manure, compost can increase the nitrate content in the soil, and therefore in fruits. Their excessive application is no less harmful than the use of mineral fertilizers.

Therefore, the main rule for using any of them is compliance with the standards established by science.
It is undesirable to use fertilizer for crops such as:
It is for these crops that saltpeter can trigger the processes of nitrate accumulation. To avoid the accumulation of undesirable substances, it is worth stopping feeding at least 15 days before harvest.
How to ensure proper storage of saltpeter?
Fertilizers have the following qualities:
- Hygroscopicity, that is, the ability to absorb moisture from the air, ammonium nitrate has a very high indicator, so it becomes damp, cakes and loses its physical properties.This can be avoided by choosing the right storage location: avoid getting the container with fertilizer wet; the room should be non-residential, well ventilated and dry.
- Each type of fertilizer is stored separately. Saltpeter is a rather dangerous explosive compound and can ignite upon contact with certain substances. Contamination of fertilizing with debris: scraps of paper, fabric leads to the appearance of hot substances, which, upon contact with saltpeter, ignite and even detonate.
- Caking often brings great convenience to summer residents and gardeners. They have to put a lot of effort into breaking up the clods of fertilizer and crushing them into small particles. The most convenient way is to sift through a large sieve. Or put them in a strong bag and crush them with gentle blows, since saltpeter can detonate!
- Spreadability is a useful quality that makes it easy to distribute substances throughout the area during fertilizing. To avoid dampening and mixing of granules into a continuous mess, store fertilizers in a container with a tightly closed lid.
At the same time, the compounds do not lose their main properties as fertilizers; only the ability to quickly and conveniently be applied to the soil is lost.
The packaging or container must be made of plastic or enameled metal. The most important condition is complete isolation from moisture. According to safety precautions, it is prohibited to use open fire near ammonium nitrate.
Today, crop production is quite difficult to do without mineral nitrogen fertilizers. Thanks to them, gardeners and flower growers can always get a good harvest.
Ammonium nitrate is one of the most inexpensive types available to everyone. feeding. This explains its great popularity and ubiquity of use.
For more information about the use of nitrogen fertilizers, see the video:













Comments
Nitrate is a nitrogen fertilizer and it is applied to the soil to feed seedlings, because nitrogen gives seedlings energy and they grow quickly. When the fruits appear, ammonium nitrate is not needed.
Ammonium nitrate was used in the garden at our summer cottage. However, they decided to use exclusively organic fertilizers and subsequently abandoned the use of nitrate.