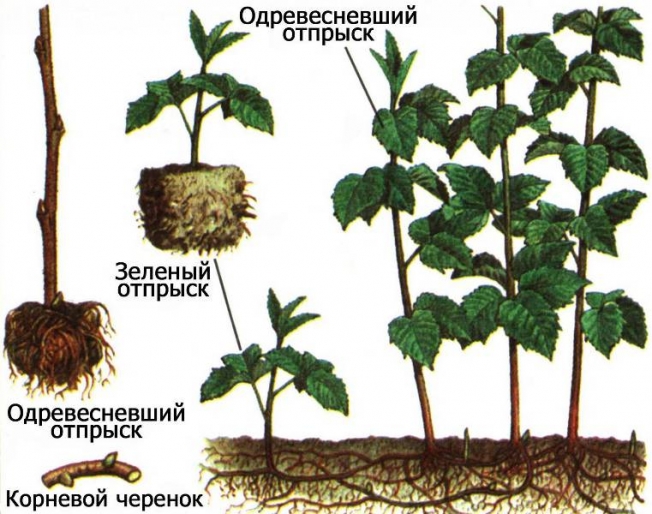
Methods of propagation of raspberries, cuttings, methods of netting, dripping and Scotch

Raspberries are a delicacy for adults and children, so no one misses the opportunity to plant this shrub in their garden.
We propose to consider the most productive and frequently used methods of propagating raspberries; step-by-step instructions for carrying out these manipulations are provided.
Content:
- Raspberry propagation methods
- Dropping
- Nettle method
- Lignified cuttings
- Scottish way
- Use of seed material
- Accelerated plant propagation
- How berries reproduce in nature
- Recommendations for propagating yellow raspberries
Raspberry propagation methods
Experts do not identify a specific type of raspberry cultivation, since each method has both advantages and disadvantages. The propagation process is influenced by many factors: raspberry variety, weather conditions, selection of planting material, planting location, age of the plant.
As for the last factor, for growing raspberries it is worth using a two-year-old bush.
The most effective methods of propagation are the following:
- cuttings;
- seeds;
- dropwise;
- dividing the bush;
- layering;
- root shoots.
Propagation by seeds is carried out rarely and only for one purpose, to develop a new variety. The most popular method is cuttings or root shoots.
There is one specificity - when the central and main part of the bush is removed during pruning, many young shoots will grow on the remaining branches. This pruning is carried out in order to quickly propagate the crop; it will not be possible to collect a harvest this year, but it is just right to collect enough planting material.
Dropping
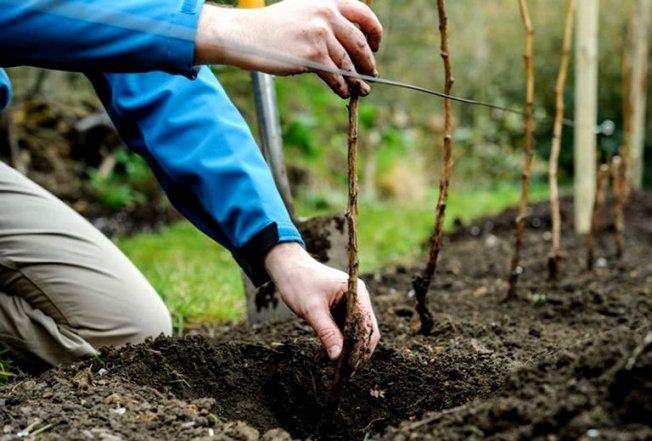
This manipulation is carried out in early March. Overwintered and annual shoots are used for digging.
Scheme of the procedure:
- Choose a suitable shoot; it must be healthy and flexible. Make measurements and marks on the ground where digging will subsequently take place.
- In the marked area, dig up the soil and mix it with sand and peat.
- Make a hole for escape; a depth of ten to fifteen centimeters is considered optimal. Fill the ditch with water and wait until it is absorbed into the soil.
- The selected branch is bent to the ground, all side leaves and branches are trimmed with garden shears. It is necessary to leave only those shoots that grow upward.
- On the remaining branches near the base, the stem is scratched. To do this, neat longitudinal and oblique cuts are made, no more than two millimeters deep. It is advisable to treat the cuts with Kornevin.
- The shoot is placed in the hole, pinned with wire staples and covered with soil on top. The crown should be left outside, approximately twenty centimeters long. The top is positioned vertically and tied to a rod or peg.
- Watering and mulching are carried out.
If the manipulation is carried out in accordance with the requirements, then the seedling can be separated from the mother bush in the fall.Some carry out this procedure in the summer, using green shoots, then the seedling will be ready by next autumn.
Nettle method
When choosing this technique, use a young plant, the stem of which appeared in early spring. The method is called nettle method, since the stem is very similar to nettle.
The height of young shoots is no more than 10 cm, however, two fully developed leaves must be present.
The action plan is:
- Remove the soil from the young stem and cut off the shoot to the very base. The shoot height will be from 3 to 5 cm.
- The incision must be disinfected with stimulants: Epin, Heteroauxin or Kornevin.
- Specially prepare a peat substrate with the addition of sand in a one-to-one ratio, or on the basis of sand, turf soil and peat (sand in this case is used half as much as the other ingredients). The soil is moistened.
- We plant the plant in the substrate so deep that the white part and one centimeter of the green part are hidden in the ground.
- To create a greenhouse effect, cover the sprout with half a plastic bottle, half a liter jar or film. On a large scale, greenhouses with a special fog-forming installation are used for such manipulations.
It is worth understanding that the sprout does not have roots and does not have the ability to receive nutrients from the soil, so it is necessary that condensation falls on the leaves and feeds the stem.
Let's watch a video about propagating raspberries using the nettle method:
To carry out this method, it is worth selecting areas protected from the sun, for example, near a fence, under bushes and trees. Installed greenhouses in direct sun will burn the shoots. The optimal temperature is considered to be from plus twenty to plus twenty-six degrees.
Over the course of 30 days, the sprouts will take root and leaves will grow on the stem.
Lignified cuttings
Harvesting is carried out in the autumn, from mid-October to mid-November. Branches that bear fruit are used; by the specified time they will be covered with hard bark.
Escapes cut into equal cuttings. Be sure to remove all leaves. Buds have already formed on the cuttings, since the growing season has ended, and it is from the buds that new leaves should appear in early spring.
Manipulation can be carried out in several ways:
- In the fall, the trimmings are carefully tied together and placed in a container with sand and wet shavings. If several varieties are used at the same time, then they are divided into bunches and labeled. In the spring, planting is carried out on the garden plot.
- Woody cuttings are wrapped in plastic film or damp cloth. In both cases, it is important to make small holes for ventilation. Place the planting material in the cellar or put it in the refrigerator. Temperature and humidity are important: the temperature should be at least minus two, maximum plus 2 degrees, and the humidity should be between 65 and 70%. In the first month of spring, cuttings are planted on a windowsill, in a greenhouse or in a greenhouse using the nettle method.
- The third method involves cutting cuttings, but they are not prepared for the winter. The prepared material is immediately planted in open ground, the cuttings are deepened so that the tops of the heads, on which there are two buds, stick out from the ground. The cuttings must be covered for the winter with agrofibre, reeds or spruce branches. You can use other raw materials, the main thing is to allow air to pass through. Film is not suitable in this case.
You can use one of these methods or experiment with all of them at once.
Scottish way
The Scottish method of propagating raspberries is the most effective and productive, as it is possible to obtain many healthy, productive seedlings in a short period of time.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- In early spring, sawdust, humus and peat are poured onto the ground around the bush, all components are taken in equal proportions. The resulting mixture promotes the rapid formation of buds on the raspberry bush and its rhizome.
- In the fall, the roots are cut into cuttings. They are formed into small bunches, wrapped in cloth, placed in a container with wet sand and left in the basement until spring.
- Next spring, in March, the cuttings are taken out of the basement and planted in flowerpots with sand and peat. Sprouts need abundant watering. After 14 days, green shoots should emerge.
- The sprouts are replanted again, for this they now use soil with the addition of 1 part sand, 1 part peat, three parts turf, superphosphate (5 grams per 100 grams of soil) and 50 grams of dolomite flour.
After 30 days, raspberry seedlings can be transplanted into an open area; the harvest will appear in a few years.
Use of seed material
Propagating raspberries by seeds is a very troublesome and difficult task; it is worth choosing this propagation method if there is a need to develop a new variety.
There are many nuances to ensure that the entire procedure is successful:
- Use ripe berries to get the seeds.
- The product is ground to form juice.
- Water is poured into the contents, mixed thoroughly, and everything that floats to the surface is drained.This manipulation is carried out many times until the water becomes clear and the seeds can be seen.
- Everything is filtered through a sieve and seeds are obtained, which are used to propagate the crop.
- The material is laid out on cotton cloth or dry paper so that the seeds dry well.
- Seeds can be used immediately for planting, or placed in a paper or plastic bag and stored in the refrigerator.
- The next step is stratification, since the seed germinates slowly. The seeds are placed in water for a day, then mixed with wet sand and placed in nylon bags. Nylon is covered with steamed sawdust or moss, lightly watered and placed in the refrigerator or basement for 3 months.
- After the specified period, simultaneously with the sand, the seeds are planted in a small box, into which moist soil no more than five millimeters thick should be poured. Sifted peat is scattered on top in a thin layer, the container is covered with glass and the box is placed in a bright, warm place where there is no direct sunlight or drafts.
- When the sprouts stretch up to 10 cm, pick them into cups. When the warm weather stabilizes outside, the seedlings can be planted in open soil, choosing an area without wind and sun.
After a few years, healthy seedlings grow; they can be left for further growth, or transplanted to another area.
Accelerated plant propagation
Accelerated propagation is considered to be the Scottish method, green cuttings and propagation of seedlings in the field. Let's look at the last option in more detail.
A trench is dug in the field, 30 to 50 cm deep, and organic matter is added as fertilizer. Lay out the roots along the length of the entire trench and water.
If the procedure is performed in the fall, it is necessary to protect the seedlings from frost; for this purpose, hilling is carried out.
As a result, using a kilogram of roots, up to one hundred healthy seedlings are obtained. The following autumn, they are dug up with careful movements to preserve the rhizome, and planted in a permanent site. Fertilizers are applied to the soil, and the next year, in the spring, in addition to one seedling, up to 8 new ones will appear.
How berries reproduce in nature
In nature, it reproduces by seeds and vegetatively.
In the second case, reproduction occurs independently. The berry grows in one place for a long time, and thanks to its roots it is constantly renewed. Eventually, the old roots disappear and new ones take hold in the new area, promoting abundant growth.
Recommendations for propagating yellow raspberries
For this crop, root suckers are chosen as propagation. Strong shoots are dug up at the end of autumn with a clod of earth and transferred to another place. The transplant site is fertilized with humus and watered.
The method of propagating yellow raspberries by cuttings is also effective. The material is prepared in advance, in spring or autumn, and then stored in the basement, covered with nutritious soil. When roots appear on the cuttings, plant them in separate containers. When the leaves bloom on the shoots, the seedlings are transplanted into the garden.
Propagation using seeds is not recommended. It is easier to buy new seedlings or carry out the above propagation methods.
So, raspberries propagate in many ways, all of which, if the recommendations are followed, give a positive result. When choosing a method, it is important to take into account the variety and skills of the owner.
Let's watch a video about growing raspberries with roots: