Nightshade pest from Colorado or who the Colorado potato beetle is, methods of controlling it

The Eurasian continent was once free of the Colorado potato beetle. The homeland of the malicious foreign pest of nightshade crops is America. Its name itself suggests that its history is somehow connected with the American state of Colorado. Indeed, this beetle completely destroyed the plantings potatoes in this state in the mid-19th century. We will try to figure out why the Colorado potato beetle is terrible, methods of combating it, and whether it is possible to protect the area from this pest.
Content:
- Colorado potato beetle, zoological description
- Methods for controlling the Colorado potato beetle
- Traditional methods and prevention of infestation of plantings with the Colorado potato beetle
Colorado potato beetle, zoological description
According to zoological taxonomy, the Colorado potato beetle belongs to the Leaf Beetle family from the order Coleoptera. This beetle is native to the northern and eastern regions of Mexico. Here the beetle fed on wild nightshade and tobacco. Apart from the Colorado potato beetle, only one or two closely related species could feed on the terrestrial parts of these plants.
The rest of the insects walked around or flew around the nightshade. This is due to the high content of corned beef alkaloid in its leaves. The size of adult individuals reaches 1 cm or slightly more. The width of the beetle's body is about 0.6 cm. The body shape is oval, the back is convex, yellow-orange in color. Each elytra has five black stripes.
This feature formed the basis for the Latin name of the beetle - ten-lined. The wings of the Coloradoan are well developed. It is capable of flying over long distances. Despite the fact that the beetle's homeland is Mexico, it tolerates the climate of European countries well. It must be said that the beetle appeared in Europe at the end of the 19th century. It was brought from overseas along with household goods.

While there was war in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century, the beetle multiplied and established itself in the famous French province of Bordeaux. In a few decades bug mastered Europe and the western regions of the USSR.
It was quite difficult to fight it, since wintering adults burrowed to a depth of 0.3-0.4 m. And if females fertilized in the fall went to winter, then as soon as seedlings of nightshade crops appeared in the fields, the female would immediately lay They have pale yellow eggs. The important thing is that the eggs are attached by the female beetle from the underside and are hardly noticeable from above.
A person begins to sound the alarm when the emerging larvae begin to actively destroy the leaves of potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, and petunias. As they feed, they grow and change color from brown to pink. Here they become more noticeable, but it’s too late.
A new focus of damage to agricultural crops by Colorado potato beetle larvae has already formed. As the larvae mature, they move to neighboring plants.
And at the age of three weeks they burrow into the soil where pupation occurs. An insect that emerges from a pupa can get out, or it can remain in the ground until the next season. The female can lay up to 70-80 eggs at a time.
And during the season it will give birth to 300-500 new beetles.The pest poses a great danger not only to potatoes, but also to other vegetables from the Solanaceae family. It is difficult to fight, as it is very tolerant to most pesticides.
In addition, detect and destroy wintering in soil It is very difficult for adult beetles. The beetle has natural enemies, but sometimes due to differences in life cycles, they do not have time to cause significant harm to the population. In some cases, the beetle manages to practically destroy the plantings. Let's try to figure out what methods can be used to defeat this dangerous pest.
Methods for controlling the Colorado potato beetle
Many chemical and mechanical methods of controlling the Colorado potato beetle may have varying effectiveness, but none of them are absolutely reliable. However, it is possible and necessary to fight the pest. This is where biological control measures can come to the rescue.
Edovum
The six-legged edowum is a natural enemy of the Colorado potato beetle. Of course, it cannot defeat an adult, but this insect can cope with laying eggs. The female edowum lays her offspring in the eggs of the Colorado potato beetle. One individual can infest up to 1000 pest eggs with its offspring.
Edowum is especially effective at infecting the second generation of beetles. To combat pest a technology for growing edovum crops has been developed to supply potato farms. Breeding predatory ground beetles, lacewings and some other insects also helps fight foreign beetles.
Chemistry against the Colorado potato beetle
Insecticidal drugs of the last century caused the beetle to quickly adapt. Therefore, it is currently advisable to use new generation drugs:
- "Bankol" - the drug is obtained from annelid sea worms, their poison is very effective against the Colorado potato beetle
- "Regent" - the drug affects the pest at any stage of development
- "Commander" - its action is similar to the previous remedy
- "Aktara" is a systemic insecticide that acts on the beetle through plant tissue
Video about fighting the Colorado potato beetle:
The drugs must be used strictly according to the instructions.
Traditional methods and prevention of infestation of plantings with the Colorado potato beetle
In small plantings of nightshade crops, mechanical collection of larvae gives good results. All collected pests you need to put it in glass jars, and then fill it with a concentrated solution of table salt. If the larvae have not yet appeared, then the discovered clutches can be removed along with the leaves. In addition, you can use the following control methods:
- planting marigolds, marigolds, nasturtiums among potatoes
- spraying with a mixture of laundry soap and ash, take a bar of soap and two liters of ash per 10 liters of water
- spraying with urea, just dissolve 100 g of the substance in 10 liters of water
- spraying with an aqueous infusion from the Colorado beetles themselves, for this the insects are collected, placed in a jar and filled with water, closed with a lid, after 5-6 days the poisonous infusion is ready
Prevention
Currently, a good prevention is to plant varieties bred without GMOs, which the Colorado potato beetle does not eat, since they have coarser ground parts. The arrangement of grooves - traps along the plantings, the larvae cannot overcome due to the inclination of the walls.
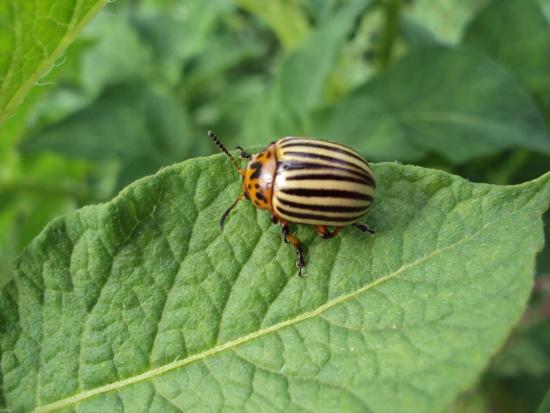

Purchasing healthy planting material, digging up the soil and turning over the layers in the autumn. Sometimes, for inexplicable reasons, it happens that the Colorado potato beetle disappears and ceases to harm landings.