Why weevils are dangerous, weevil control and prevention

Weevils are one of the most numerous families from the order Coleoptera. More than 50,000 species of weevils have been identified and identified worldwide. Almost 5,000 different species of these beetles are found in Eurasia. All of them, to one degree or another, harm wild and cultivated plants.
If no measures are taken to reduce the number of these beetles, they can cause significant damage to both forest plantations and agricultural plantings, gardens, berries, grains, and vegetable crops. Struggle with weevils should be carried out taking into account the biological characteristics of insects. Let's try to figure out what weevils look like and their life cycle.
Content:
- Weevils, general description of the family
- Description of the most common types of weevils
- How to deal with weevils, preventing infection
Weevils, general description of the family
Given the numerous species, weevils can differ from each other:
- sizes
- coloring
- body shape
- food addictions
What all species have in common is the structure of the front part of the head, which, due to its elongated shape, is called the rostrum. Because of this, weevils got their name in Russian. The second, popular name is elephants. It is important to divide the family into:
- long-proboscis
- short-proboscis
From the names it is clear that insects differ in the length of the rostrum.In addition, the larvae of these varieties differ in food preferences. Elephant larvae are usually located on leaves and on parts of the plant above the surface soil. Short-proboscis animals primarily live in the ground.
The mouthparts of adult beetles are located at the end of elongated proboscis. The proboscis of most species has special elongated indentations into which the beetle's antennae are placed. In many species, females and males differ in size and appearance, often females are larger, with a longer and more curved proboscis. There are species that have no sex differences in appearance.
Female weevils have adapted to making depressions in plant tissue and laying eggs there. The weevil's clutch contains from one to three dozen eggs. Long-proboscis species very often lay eggs inside nuts, apples and other fruits.
The larvae of short-proboscis weevils develop in the soil, where they feed on roots. The body shape of weevils can differ significantly; some beetles are rod-shaped, while others have a thickened round, diamond-shaped or pear-shaped body. Their coloring also differs; there are weevils with a single color, with a metallic blue or green sheen, or matte, with spots and other patterns. Weevil larvae have a thickened, fleshy, legless body. Most often curved in shape. The body color of the larvae is very different:
- white
- red
- cream
- yellow
- brown
The danger of weevils is that at any stage of their development they feed on plants. To apply effective control measures, you need to know about the characteristics of the most common beetles -pests from the Weevil family.
Description of the most common types of weevils
Raspberry flower beetle
The pest has a black body 3 mm long. Longitudinal grooves and gray fibers are noticeable on the wings. The larvae are white. The larvae's head is yellow-brown. The pupae are white at the initial stage, but dark before the beetles emerge. The winter is spent under plant debris. With the appearance of the first greenery, they begin to feed. As soon as the raspberries or strawberries form buds, the females gnaw through the side and lay one egg in the bud.

After this, the female also gnaws the peduncle, after which it easily breaks off and the bud with the egg falls to the ground. After a week, a larva emerges from the egg. She lives and feeds inside the bud for just over three weeks. Then pupation occurs. And after 10 days, a young raspberry flower beetle emerges. Mass release can be observed in mid-July. And by the end of the month the beetle is looking for shelter for the winter.
The flower beetle is dangerous because one female lays about a hundred eggs. First they damage all varieties of strawberries, from early to late, then they move to raspberries.
Southern gray weevil
This representative of the family is dangerous due to its omnivorous nature and ability to fly. It begins to feed on the first greenery, most often on winter crops. Switches to beets, corn, sunflowers. Even weeds are actively affected. The body is 7-8 mm long, the color is dark, the wings are well developed.
After wintering, which the beetles spend in the soil, most often in the field after corn at a depth of about 50 cm, they emerge from the soil and mate after ten days. After which the female lays about three hundred eggs in the soil. The eggs are located at a depth of 20 cm, in small groups of up to 10 eggs. The larvae feed on plant roots for 60 - 70 days. They spend about 20 days in the pupal stage. Adults appear in early August.
Stone beetle
The stone fruit beetle is a dangerous pest of stone fruit crops. Adult beetles feed on buds and leaves. The larvae live inside stone fruits:
- plums
- bird cherry
- cherries
- cherries
The size of the beetles is 4-5 mm, the color is yellow-brown, without shine. In the spring, when the earth warms up to +9, overwintered beetles emerge from soil and begin to actively eat. As soon as the young fruits begin to set, the female gnaws through the still soft shell of the seed and lays an egg. All development occurs inside the bone. In order for a young beetle to get out, it has to gnaw through the hard shell for about two days.
Video about weevils on raspberries:
After the flower beetles leave the fruit, they move into the soil and prepare for the winter. In addition to the above, significant harm can be caused by weevils that feed on coniferous and deciduous trees, as well as granary weevils; they damage grain crops both during their growth and grain stored for storage. Let's try to figure out how to combat these pests and preventive measures.
How to deal with weevils, preventing infection
Chemicals against weevils
The most effective control method remains the use of chemicals for spraying garden and vegetable crops.
Aktellik
It is effective to spray the following crops with Actellik:
- strawberries
- raspberries
Two ml of the drug are diluted in two liters of water and immediately sprayed on the plantings. This amount is enough to treat an area of 10 square meters. After 6-7 days, another treatment is carried out. The use of the drug 20 days before the start of harvest is not allowed. It is important to remember that this drug should not be used together with Bordeaux mixture.
Karbofos
This drug effectively resists weevils that live on:
- raspberries
- plum
- apple tree
- pear
- cherries
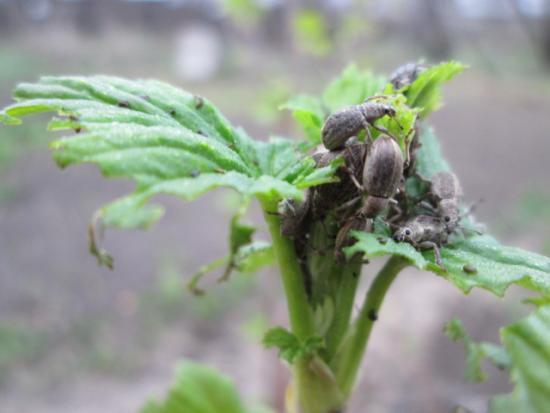

The solution is prepared at the rate of 60 g of the drug per 6 - 8 liters of water. Considering that the protection lasts about 10 days, a second treatment is needed after this time. Mechanical method of control To do this, newspapers are laid out under the plants in the evening. In the morning the bushes need to be shaken. After which the newspaper is immediately rolled up along with the fallen pests and is burned.
Traditional methods and prevention
Ash is a good way to repel weevils. In spring it is scattered in a thick layer around bushes and trees. The weevils will also be repelled by fragrant grass laid out in the beds and between the rows. Wormwood is suitable for this. Timely removal of plant debris, removal of weeds, as well as maintaining the correct proximity of crops and their crop rotation, can prevent weevil damage to plants.