How to make a winter greenhouse, work order, useful tips

The construction of any structure begins with the selection of a project. For an inexperienced vegetable grower, the question of how to make a winter greenhouse can be very difficult: from the right choice of design, materials, and heating system. It is these factors that determine the possibility of obtaining the planned harvest.
Content:
- Types of winter greenhouses
- The procedure for performing work during the construction of a standard building
- Construction of a greenhouse with earthen filling
- Gable option, what are its advantages
- Features of a budget double-coated design
- Organization of heating
- Tips from the master: how to avoid soil freezing
Types of winter greenhouses
Winter buildings are significantly different from seasonal ones. First of all, you need to decide on their functionality. Growing herbs, grapes, mushrooms or vegetables, exotic plants or flowers will require different design solutions.
Based on their location, they are divided into several types:
- deepened into the ground;
- located on the surface;
- erected on the roofs of courtyard buildings: garages, sheds. baths
According to the heating system option, heated:
- wood stove heating;
- electricity;
- environmentally friendly biofuel.
According to the architectural solution, winter greenhouses can be:
- wall-mounted, the most economical, having a common wall with the house, but not requiring a large building area;
- arched, which are usually used for growing herbs, vegetables, and other low-growing crops;
- with one, two and three-pitch roofs that can withstand heavy loads created by snow.
All of them are functional and suitable for year-round use in any climate zone, and can have a significant area. Using the soil growing method or hydroponics, they can grow large volumes of produce.
The most popular among vegetable growers are thermos greenhouses, which allow them to obtain high yields with minimal maintenance costs. A special feature of the design is its complete isolation from atmospheric influences and cold soil.
We indicate the advantages and disadvantages of such a structure in Table 1.
| Advantages of a thermos greenhouse | Flaws |
| Possibility of operation in any climate zone | Construction costs |
| Receiving a high quality harvest throughout the year | The need for proper arrangement of heating and ventilation systems, communications |
| Possibility to save energy due to high thermal insulation characteristics | |
| Using the “thermos” effect - the ability to retain heat received from the sun for a long time, the rays of which can penetrate inside almost unhindered | |
| Possibility of growing crops that require growing conditions |
Taking into account the positive aspects, it can be argued that a thermos greenhouse is the optimal solution for those who want to produce vegetables and herbs all year round for the needs of the family and for sale.
Before you make a winter greenhouse, you need to realize that its construction will require considerable funds, the structure must be of good quality, equipped with heating and lighting.The advantage of this option is the ability to obtain a harvest regardless of weather conditions over a long period of time.
The procedure for performing work during the construction of a standard building
Construction is carried out in several stages, the first of which is installation of the foundation.
The choice of its type depends on:
- size of the structure;
- depth of groundwater and the presence of a drainage system on the site;
- nature of the soil.
For a small greenhouse you can equip any type of foundation:
- brick or block;
- tape or point.
Large buildings require the laying of a concrete foundation, or one assembled from timber.
In order not to make a mistake with the depth of the pit, you should focus on the depth of soil freezing in your area, usually 80-100 cm.
To assemble the frame of a capital structure, a galvanized corner, a profile pipe, and a hat profile are used. The first, as the most durable, is recommended for use in areas where heavy snowfalls occur in winter. Aluminum structures can become deformed when exposed to strong winds and snow.
No welding is required to assemble the corner profile; the structure can be assembled using bolts. To attach the frame to the foundation, anchor bolts are used that can withstand loads and provide rigidity. Due to the difference in the heat capacity of materials, the structure is less exposed to the negative effects of high and low temperatures. It is recommended to reinforce the greenhouse frame with transverse stiffeners.
Maximum permissible snow load per 1 sq.m. the roof of such a greenhouse is 100 kg.
To cover the frame, materials are most often used, the advantages and disadvantages of which are indicated in Table 2.
| Material | Advantages | Flaws |
| Polyethylene film | Cheapness Easy to install | It breaks very quickly, especially in frosty weather with strong winds, so it is rational to use it for summer greenhouses |
| Glass | Excellent light transmission Keeps you warm | Very fragile, easily destroyed by impacts, it is rational to use a Float type coating or greenhouse glass |
| Cellular polycarbonate | Light weight Long (up to 15 years) service life The light transmittance coefficient ranges from 62 to 83%. | Tendency to thermal expansion, which requires compliance with installation rules Low abrasive resistance |
The roof shape is usually gable, with a slope of at least 20 degrees. For each specific form it is calculated individually. The indicator is very important; the load-bearing capacity of the greenhouse relative to the load of snow cover and the rate of storm water runoff depend on it.
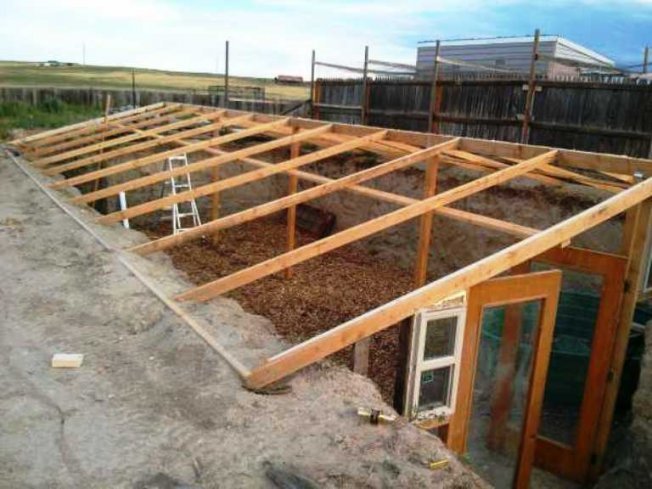
To build a gable roof, it is necessary to fix the strapping beams along the two side walls. Next, the ridge beam and paired rafters are installed.
If the frame is wooden, then the rafters are made of timber with a cross-section of 70x100 mm, the ridge and trim are made of material with a cross-section of 120x150 mm.
The roofing elements of metal structures are made from the same materials that were used for the installation of wall frames.
Let's watch a useful video about arranging a winter greenhouse:
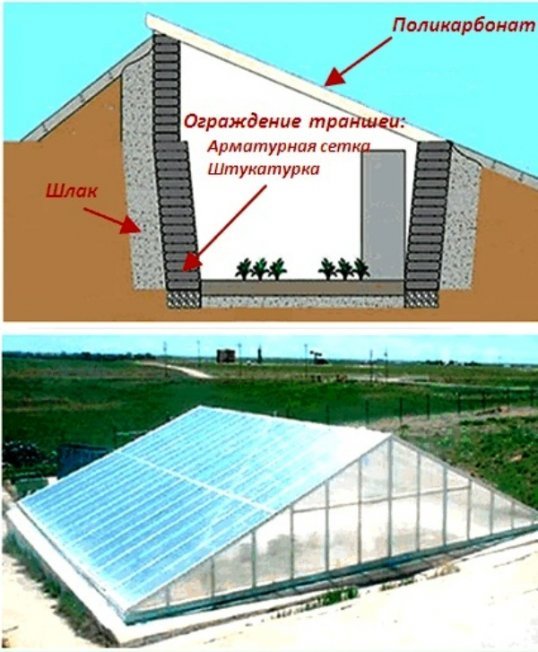
Construction of a greenhouse with earthen filling
The budget option includes the construction of a lean-to earthen building. To construct it, you will need to assemble a frame of wooden posts arranged in three rows.
Construction begins with marking and digging a pit.Next, they begin to install the racks; on the north side they should have a length of 150 cm, in the center - 170 cm, on the south - 90 cm.
The outer rows of racks are sheathed with slabs along the entire length, the middle row - only to the height of the ridges. The hole, the depth of which is 90 cm, is filled with biofuel, the upper 10-15 cm are filled with soil. The northern and southern walls are covered with soil. The southern slope of the roof is covered with a transparent roof.
To prevent heat loss at night, the glass is covered with mattresses made of straw, reeds, and film. Provided good biofuel is used, the greenhouse can be used starting from February-March for growing greens, onions, and lettuce.
Gable option, what are its advantages
A more versatile option are gable brick greenhouses, which can be used in climate zones with harsh climates. Such structures can hardly be classified as economy class, but they can be used for many years.
Such greenhouses consist of a working area and a vestibule.
A vestibule is a utility room in which you can:
- install a heating boiler;
- place control units for irrigation, lighting, ventilation;
- store equipment, soil mixtures, fertilizers.
The length of the vestibule must be at least one and a half meters, its roof must not be transparent.
Brick is used to build walls, and mineral wool or foam plastic is used for thermal insulation.
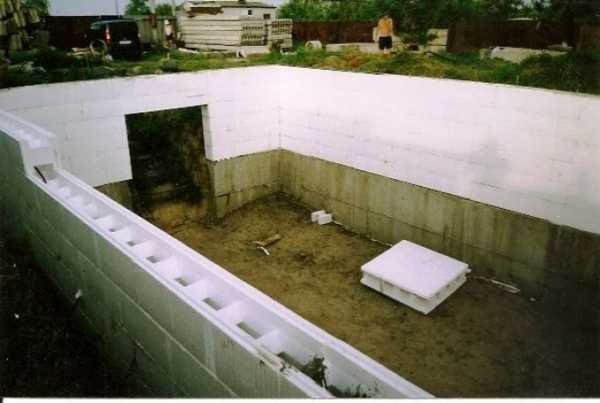
The depth of the pit during construction should be at least 80-90 cm (equal to the depth of soil freezing).
The order of work is as follows:
- a pit of a given size is dug;
- a strip foundation is poured to a depth of 80-90 cm;
- 1 brick walls are erected;
- window openings are made at a height of 60 cm above the ground level, the distance between the windows is 2-3 bricks, which will provide high-quality lighting;
- After the walls have been forced out, the roof is constructed; a gable roof with a 25-degree slope will ensure good water drainage;
- installation of strapping beams is carried out on a layer of waterproofing (you can use roofing felt); install ridge beams and rafters.
Polycarbonate or double glass with a thickness of at least 3 mm is used as roofing material.
Features of a budget double-coated design
To organize the roof of a winter greenhouse, you can use triple air bubble film. In this case, the walls can be covered with ordinary double walls.
The use of a hydrophilic film will prevent the accumulation of condensation, which is quite difficult to remove when using a double film. In addition, air bubble film is capable of transmitting an amount of light sufficient for the normal development of plants.
When organizing a winter greenhouse, one should not forget about the importance of subsoil heating.
Organization of heating
Arrangement heating systems - a very important point that requires taking into account climatic features, the type of structure chosen and its dimensions. With a greenhouse area of about 15 sq.m, stove heating can be used. A stove is installed in the building and heated with coal, gas or wood, pellets. It is not recommended to plant plants near the stove; the space near it gets very hot and the plants will not feel comfortable.
It is more rational to heat large rooms with biofuel, electric heaters, and water circuits.
To organize water heating, install a boiler and lay a pipe system, either at a depth of 40 cm, or under the shelves.
Electric heating can be produced:
- by installing a "warm floor" system (cable);
- by installing heat fans (air);
- by installing special heating devices (infrared) under the roof.
The cheapest option is to use biofuels. These are various organic substances, the decomposition of which releases heat. Biofuel is placed directly on the beds, under the top layer of fertile soil.
In Table 3 we indicate the features and characteristics of commonly used biomaterials.
| Material | Maintained temperature | Duration of "service" | How does acidity affect soil? |
| Shredded rotten tree bark | +25 C | 4 months | Creates an acidic environment, acidifies the soil |
| Horse dung | + 33 C - + 38 C | 2-3 months | Creates an alkaline environment |
| Cow dung | + 20 C | 15 days | Acidity is normal, 6-7 pH |
| Wood sawdust | + 20 C | 15 days | Creates an acidic environment, acidifies the soil |
| Straw | + 45 C | 10 days | Acidity is normal |
Burnt-out biomaterial can be reused as fertilizer for garden beds.
Let's watch an interesting video on how to make a greenhouse and heat it in winter:
Tips from the master: how to avoid soil freezing
The problem is the threat of soil freezing.
Therefore, we offer several life hacks that will help prevent a negative phenomenon:
- when laying the foundation, you can use heat-saving foam blocks or adobe, with a thickness of 40 cm, such material provides the same thermal insulation as 70 cm of brickwork;
- To insulate the inside of the greenhouse, foam panels wrapped in polyethylene are installed near the ground.
Tip I. In order to maintain the soil temperature at +16 +18 C and prevent soil freezing, it is recommended in the fall to select soil to a depth of one and a half meters, lay a layer of a mixture of cow and horse manure, straw, and grass. This mass will decompose and warm the soil; metal-plastic heating pipes laid in the ground will not freeze in such a greenhouse even in severe frosts.
Council II. Watering in a winter greenhouse is best done with warm water by sprinkling. If the soil is not protected from freezing, drip irrigation can lead to the death of plants.
Council III. The vestibule allows you to retain heat and protects plants from sudden temperature changes.
Tip IV. The thickness of polycarbonate for the construction of a winter greenhouse should not be less than 10-16 mm; thinner ones are laid in two layers. It is also recommended to ensure that the joints are sealed.
Tip V To avoid sudden changes between day and night temperatures in the room, it is recommended to install large containers of water. During the day they will warm up from the sun's rays, at night they will slowly release heat.
Council VI. It is more expensive to heat a tall building, but only in such a room can a microclimate be created that is favorable for plants and comfortable conditions for human work.
Before making a winter greenhouse, you should carefully consider its design, make a drawing, and calculate the materials. It is also important to choose the right heating, watering and ventilation systems.